Smartphones, Social Media, and Their Impact on Mental Health
The impact of smartphones and social media on mental health is a multifaceted issue that has garnered significant attention in recent years. Here’s an overview of the current understanding, summarizing key findings from various sources:
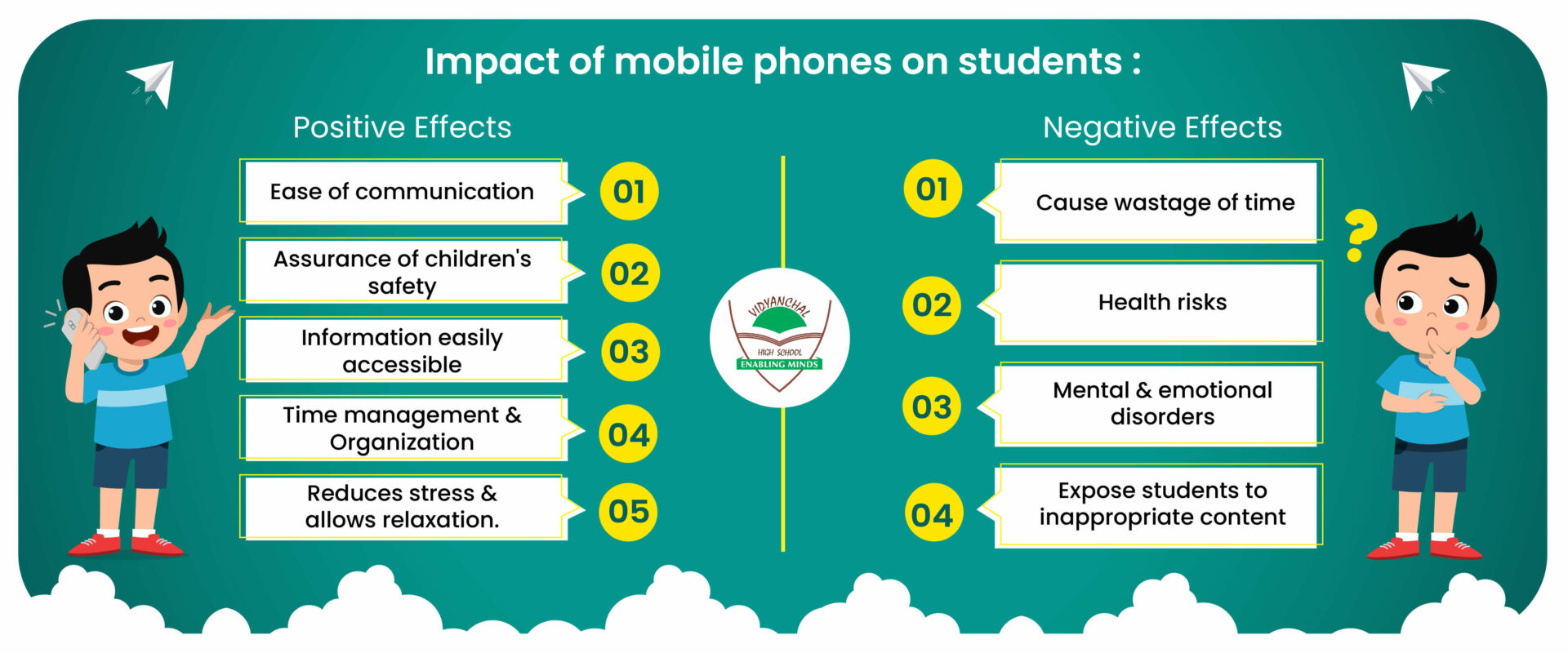
1. Positive Impacts
Connectivity and Support: Social media can help users stay connected with friends and family, which can be beneficial for emotional support and building relationships. Platforms like Facebook and Instagram can help individuals maintain social connections and access support networks.
Information and Awareness: Social media provides access to mental health resources, support groups, and information that can promote awareness and understanding of mental health issues. This can reduce stigma and encourage people to seek help.
Community Building: Online communities can offer a sense of belonging and support, particularly for those with niche interests or marginalized groups. These communities can provide emotional support and practical advice.

2. Negative Impacts
Anxiety and Depression: Studies have shown a correlation between high social media use and increased rates of anxiety and depression. Constant exposure to idealized images and lifestyles can lead to feelings of inadequacy and low self-esteem.
Sleep Disruption: The use of smartphones, especially before bed, can interfere with sleep. The blue light emitted by screens can disrupt circadian rhythms, making it harder to fall asleep and affecting overall sleep quality.
Addiction and Overuse: The design of social media platforms often encourages prolonged use, which can lead to addiction-like behaviors. This overuse can result in decreased productivity, social withdrawal, and neglect of real-world relationships.
Cyberbullying and Harassment: Social media can be a platform for cyberbullying, harassment, and negative interactions, which can significantly impact mental health, particularly among younger users.
Social Comparison: Constant exposure to curated content can lead to unhealthy social comparison. Users might compare their own lives unfavorably to the seemingly perfect lives presented by others, leading to feelings of inadequacy and dissatisfaction.
3. Research and Recommendations
Digital Detox and Mindfulness: Research suggests that taking breaks from social media or engaging in mindful social media use can help mitigate negative effects. Setting time limits and being intentional about social media activities can reduce stress and improve well-being.
Balancing Use: It’s important to find a balance between online and offline interactions. Engaging in face-to-face activities and maintaining real-world connections can help counteract some of the negative impacts of social media.
Educational Programs: Programs aimed at educating users about the potential impacts of social media and teaching strategies for healthy usage can be beneficial. Schools and workplaces can play a role in promoting digital literacy and mental health awareness.
Support Systems: Encouraging users to seek professional help if they experience significant mental health issues related to social media use is crucial. Mental health professionals can provide strategies for managing social media use and addressing any related concerns.

Moral : Use wisely
By,
Jeevitha
