Project Silica – Preserving Data for Eternity
Project Silica is a groundbreaking endeavor spearheaded by Microsoft Research with the aim of developing long-term storage technology using quartz glass. This innovative project represents a significant advancement in data storage, promising enhanced durability and longevity compared to traditional storage methods. By harnessing the unique properties of quartz glass, Project Silica holds the potential to revolutionize the way we store and preserve vast amounts of data for future generations.

Quartz glass, also known as silica glass, is renowned for its exceptional stability and resistance to environmental factors such as heat, moisture, and radiation. Unlike conventional magnetic or optical storage media which degrade over time, quartz glass offers unparalleled durability, making it an ideal candidate for long-term data storage. Project Silica leverages this inherent strength of quartz glass by etching data onto its surface using ultrafast lasers, encoding information in three-dimensional patterns.
Why we need it ?
Humanity’s need for long-term data storage continue to grow at a staggering pace. As a species, we continue to generate large amounts of high-value data (our personal histories, medical, industrial, scientific data, etc.) that is crucial to our long-term survival, with demand projected to exceed hundreds of zettabytes by 2025. Despite this need, existing magnetic media simply do not provide a sustainable and cost-effective solution. Magnetic media degrades over time, requiring significant emissions, energy, and cost to safely store long-lived data.
Project Silica is developing the world’s first storage technology designed and built from the media up to address humanity’s need for a long-term, sustainable storage technology. We store data in quartz glass: a low-cost, durable WORM media that is EMF-proof, and offers lifetimes of tens to hundreds of thousands of years. This has huge consequences for sustainability, as it means we can leave data in situ, and eliminate the costly cycle of periodically copying data to a new media generation.
How it works ?
- Encoding Data: To store digital data in quartz glass, information is first converted into a binary format of 0s and 1s, which represent the absence or presence of data bits.
- Laser Writing: A femtosecond laser, which emits extremely short pulses of light lasting only a few quadrillionths of a second, is used to etch microscopic patterns into the surface of the quartz glass. These patterns represent the binary data, with areas where the glass is modified corresponding to either a 0 or a 1.
- Three-Dimensional Encoding: Unlike traditional two-dimensional storage methods, such as CDs or hard drives, Project Silica utilizes the three-dimensional structure of quartz glass. The laser can create multiple layers within the glass, allowing for a significant increase in storage density.
- Reading Data: When it’s time to retrieve the stored data, a specialized microscope is used to examine the surface of the quartz glass. By analyzing the patterns of light reflected from the glass, the microscope can interpret the encoded data and reconstruct the original information.
- Durability: One of the key advantages of quartz glass storage is its durability. Unlike traditional magnetic or optical media, which degrade over time due to exposure to environmental factors, quartz glass is highly resistant to corrosion, temperature fluctuations, and other forms of physical damage. This makes it an ideal medium for long-term data storage, potentially lasting for tens of thousands of years.
Advanced Data Inscription and Retrieval Techniques
They are using different technologies to write and read the data: ultrafast femtosecond lasers to write, and polarization-sensitive microscopy using regular light to read. As a consequence, the Silica storage system guarantees true airgap by design for the storage media; it’s physically impossible to accidentally overwrite data during reading, as there is simply not enough power to modify the glass material. The mechanical design of the media library also makes it impossible for media to find its way back into a writer, further guaranteeing the security of archived data for its entire lifetime.
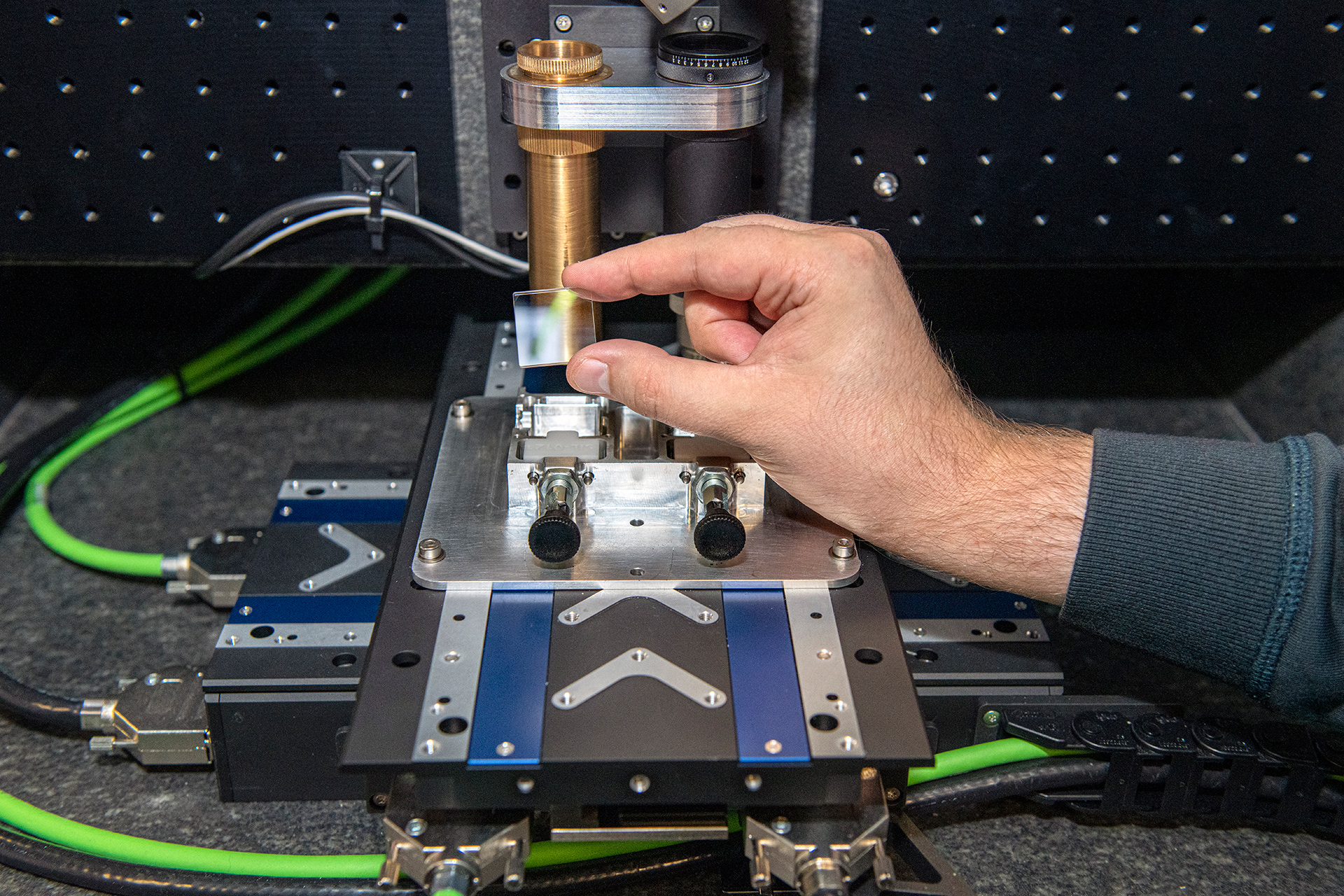
Storage Technology
As a storage technology, Project Silica boasts volumetric data densities surpassing current magnetic tapes, with raw capacities exceeding 7TB in a glass platter the size of a DVD. Leveraging beam steering of the laser, the system achieves system-level aggregate write throughputs comparable to contemporary archival systems. In essence, Project Silica emerges as a beacon of innovation, offering not just a storage solution but a testament to the boundless possibilities of human ingenuity in addressing the challenges of data preservation in the digital age.
Pros:
- High Data Density: Project Silica offers volumetric data densities that surpass current magnetic tapes, enabling the storage of vast amounts of information in a compact form factor.
- Durability: Quartz glass, the medium used in Project Silica, is highly resistant to environmental factors such as heat, moisture, and radiation, ensuring the long-term preservation of stored data.
- Longevity: With lifespans ranging from tens to hundreds of thousands of years, Project Silica provides a sustainable solution for long-term data storage, reducing the need for frequent data migrations and maintenance.
- Security: The design of Project Silica guarantees true airgap for the storage media, making it physically impossible to accidentally overwrite data during reading. Additionally, the mechanical architecture prevents media from reentering the writing process, enhancing the security of archived data.
- Innovation: Leveraging cutting-edge technologies such as ultrafast femtosecond lasers for writing and polarization-sensitive microscopy for reading, Project Silica exemplifies innovation in data storage, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in the field.
Cons:
- Cost: While quartz glass offers durability and longevity, the initial investment in Project Silica technology may be higher compared to traditional storage methods, potentially limiting its accessibility for some users or organizations.
- Limited Adoption: Despite its potential benefits, widespread adoption of Project Silica may be hindered by factors such as industry inertia, regulatory considerations, and competing technologies, slowing its integration into mainstream storage practices.
- Environmental Impact: While Project Silica offers sustainability benefits in terms of reduced energy consumption and resource usage over time, the manufacturing and disposal processes for quartz glass could still have environmental implications that need to be carefully managed.
Project Silica represents a quantum leap in data storage technology, offering a trifecta of durability, efficiency, and sustainability. By harnessing the inherent strengths of quartz glass, this pioneering project paves the way for a future where data can be preserved indefinitely, transcending the limitations of traditional storage methods. As society grapples with the challenges of digital preservation, Project Silica stands as a beacon of hope, showcasing the transformative power of human ingenuity in safeguarding the wealth of information that defines our collective history and shapes our future endeavors.