Edge Computing
Introduction:
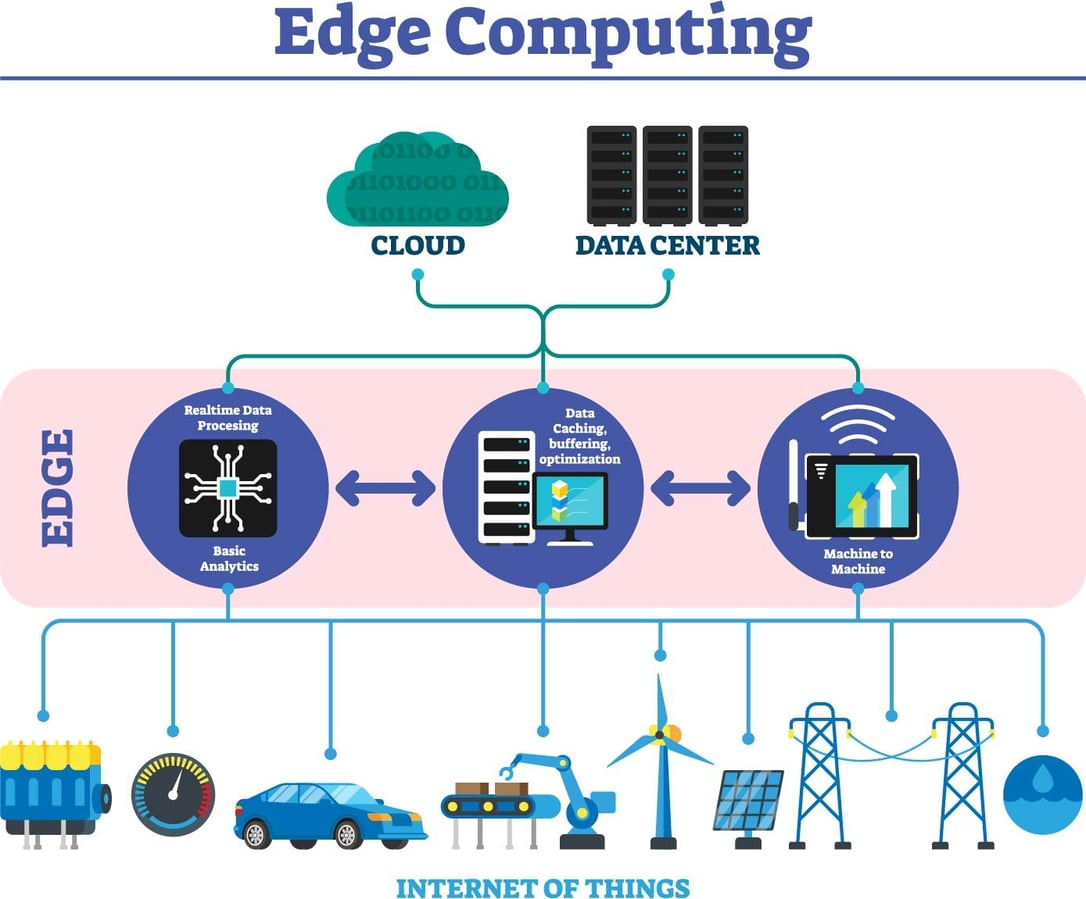
Edge computing is a cutting-edge technology that aims to bring computing resources closer to where data is generated, processed, and used. Instead of relying solely on centralized data centers, edge computing distributes computing power to the “edge” of the network, which includes devices like smartphones, smart appliances, and Internet of Things (IoT) devices. This article explores the advantages and disadvantages of edge computing and discusses its promising future.

Advantages of Edge Computing:
- Low Latency: Edge computing reduces the time taken for data to travel from the source to the cloud and back, leading to lower latency. This is crucial for real-time applications like autonomous vehicles and industrial automation, where even a slight delay can have significant consequences.
- Bandwidth Efficiency: By processing data locally, edge computing reduces the need for transferring large volumes of data to centralized data centers. This helps in optimizing bandwidth usage and eases the burden on the network infrastructure.
- Improved Reliability: Edge computing can function even in the absence of a stable internet connection or during network outages. Since data processing occurs at the edge devices, critical services can continue to operate independently, ensuring higher reliability.
- Data Privacy and Security: With edge computing, sensitive data can be processed locally without being sent to the cloud. This enhances data privacy and reduces the risk of unauthorized access or data breaches during transit.
- Scalability: Edge computing allows for scalable solutions by distributing computing resources across a network. As the number of edge devices increases, the overall computing capacity of the network can grow, accommodating expanding needs.
Disadvantages of Edge Computing:
- Limited Processing Power: Edge devices usually have limited processing capabilities compared to powerful data centers. This may restrict the complexity of applications that can be run on these devices.
- Maintenance Challenges: Managing a large number of dispersed edge devices can be challenging. Ensuring consistent updates, security patches, and maintenance might require substantial effort and resources.
- Interoperability Concerns: The lack of standardized protocols and interfaces in the edge computing ecosystem can hinder seamless communication between different devices and platforms.
- Costs: Implementing edge computing infrastructure might involve higher upfront costs, especially for deploying edge servers and edge-specific software.
The Future of Edge Computing:
The future of edge computing appears promising as it continues to evolve and mature. As more devices become connected and the volume of data generated increases, edge computing will play a crucial role in meeting the growing demands of various industries. Some key aspects of its future are:
- 5G Integration: The deployment of 5G networks will significantly enhance edge computing capabilities, providing faster data transfer and reduced latency, making it more feasible to handle advanced applications.
- AI and Machine Learning at the Edge: Edge computing combined with AI and machine learning will enable devices to process data locally and make intelligent decisions without constant reliance on the cloud, opening new opportunities for smart automation and predictive analytics.
- Industry-Specific Applications: Various industries, such as healthcare, transportation, and retail, will benefit from edge computing’s ability to process data locally, ensuring real-time insights and improving overall efficiency.
- Edge as a Service (EaaS): Edge computing may evolve into a service-based model, allowing businesses to access and utilize edge resources on-demand, reducing the need for substantial upfront investments.
Conclusion:
Edge computing represents a paradigm shift in the way we handle data and process information. Its advantages, such as low latency, improved reliability, and data privacy, make it an appealing option for diverse applications. However, challenges like limited processing power and interoperability need to be addressed. Despite these challenges, the future of edge computing looks promising, especially with the integration of 5G, AI, and the emergence of industry-specific applications. As technology continues to advance, edge computing is set to revolutionize the way we interact with smart devices and pave the way for a more efficient and connected world.